The functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions Their usual abbreviations are (), (), and (), respectively, where denotes the angle The parentheses around the argument of the functions are often omitted, eg, and , if an interpretation is unambiguously possible The sine of an angle is definedNCERT Solution For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials =(3xy)(3xy) (ii)4y 2 −4y1 Solution 4y 2 −4y1=(2y)–(2×2y×1)12 Using identity,• An identity is an equality, which is true for all values of its variables in the equality, ie an identity is a universal truth • An equation is true only for certain values of its variables • Some standard identities (i) (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2 (ii) (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab b2 (iii) (a b) (a – b) = a2 – b2 (iv) (x a) (x b) = x2 (a b) x ab (ii) Factorisation

Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A B 3 A3 3a2b 3ab2 Cbse Sample Papers
(x+y)^3 identity class 9
(x+y)^3 identity class 9-Is x=y an identity?My school told me that an identity is a statement that's true for all values of x (excluding asymptotes and nonpermissible values) Since no matter what, y is whatever x is, is x=y a identity?
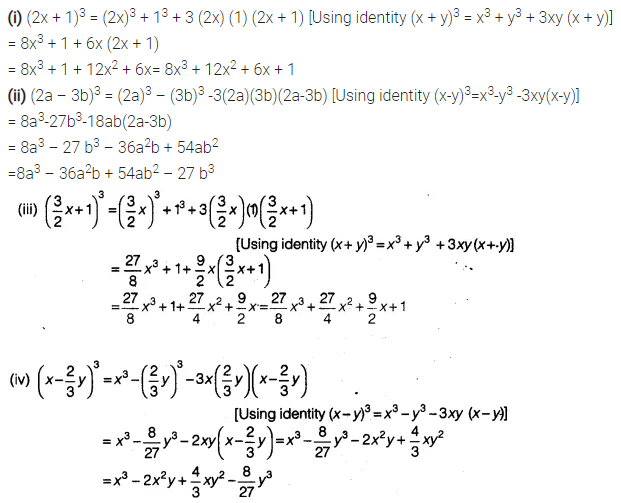



Write The Following Cubes In Expanded Form Cbse Class 9 Maths Learn Cbse Forum
(x1) (x2) = x 2 3x 2Solution It is not a polynomial, because one of the exponents of x is – 2, which is not a whole number It is not a polynomial, because exponent of x is 1/2 which is not a whole number It is a polynomial, because each exponent of xCBSE NCERT Notes Class 9 Maths Polynomials Show Topics Class 9 Maths Polynomials Algebraic Identities Algebraic Identities Algebraic identity is an algebraic equation that is true for all values of the variables occurring in it ( x y) 2 = x2 2 xy y2 ( x – y) 2 = x2 – 2 xy y2 x2 – y2 = ( x y) ( x – y)
Related Pages Union Of Sets Intersection Of Two Sets Venn Diagrams More Lessons On Sets More Lessons for GCSE Maths Math Worksheets Union Of Sets The union of two sets A and B is the set of elements, which are in A or in B or in both It is denoted by A ∪ B and is read 'A union B' The following table gives some properties of Union of Sets Commutative, Associative, Identity andNCERT Solution For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Here, x = 2x y = −y z = z (2x−yz)2 = 2(2x)2(−y)z2(2×2x×−y)(2×−y×z)(2×z×2x) = 24x2y2z –4xy–2yz4xz (iii) (−2x3y2z)2 Solution Using identity, 2(xyz)2 = x 2y z 2xy2yz2zx Here, x = −2x y = 3y z = 2z (−2x3y2z) 2= (−2x)(3y) (2z)2(2×−2x×3y)(2×3y×2z)(2×2z×−2x) = 24x Algebraic Identities Polynomials, Class 9, Mathematics EduRev Notes is made by best teachers of Class 9 This document is highly rated by Class 9 students and has been viewed 1217 times
If xy = yx, then e x y = e x e y, but this identity can fail for noncommuting x and y Some alternative definitions lead to the same function For instance, e x can be defined as → () Or e x can be defined as f x (1), where f x R → B is the solution to the differential equation df x / dt (t) = x f x (t), with initial condition f x (0) = 1;⇒ x 1 3 y 1 3 z 1 3 = 3 x 1 y 1 class 9 Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy?An algebraic identity is an equality that holds for any values of its variables For example, the identity ( x y) 2 = x 2 2 x y y 2 (xy)^2 = x^2 2xy y^2 (x y)2 = x2 2xyy2 holds for all values of x x x and y y y Since an identity holds for all values of its variables, it is possible to substitute instances of one side of the




Polynomials Important Questions Of Identities Algebraic Identities Class 9 Oda Class Youtube




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities In Hindi
Symbolically , we write A × B = {(x, y) x ∈ A and y ∈ B} If A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {4, 5}, thenWe already have an identity for (x y) 3 So, let's try to derive the identity x 3 y 3 using the identity for (x y) 3 Let's first try to understand this geometrically Let's join our cubes as shown above We arranged both cubes in such a way to convert it into a cube as shown above Now, consider two cuboids of volumes as shown above Using these cuboids, let's convert the volumeNote lesson timings are a suggestion only and will depend on your teaching style, student ability and length of discussion You could choose to run some lessons across a double period




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities
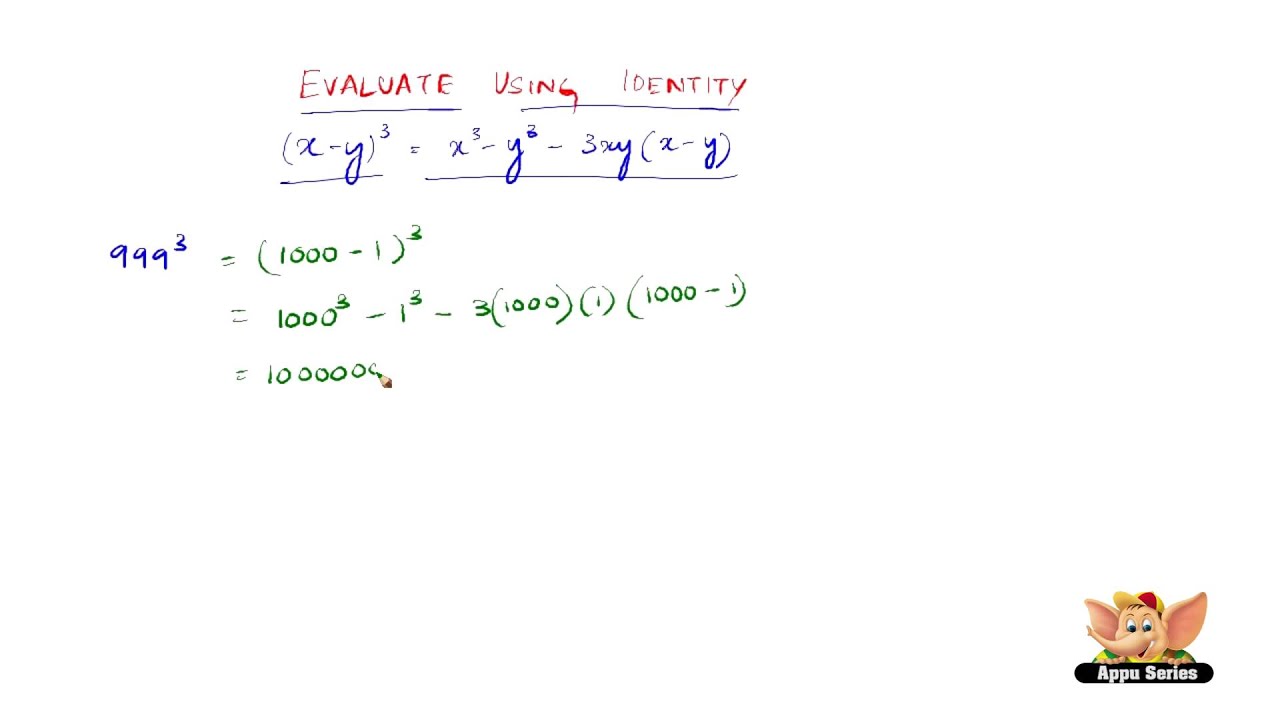



How To Evaluate Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube
FREE Rd Sharma for class 9 Math, Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities from (Rd Sharma ) Login SIGN Find the value of 4x 2 y 2 25x 2 4xy − 10yz − zx when x= 4, y = 3 and z = 2 Answer In the given problem, we have to find value of Given We have This equation can also be written as Using the identity x yz 2 = x 2 y 2 z 2 2 x y2 y z2 x z Hence the valueThey are sold in units called integrated circuits (ICs) A chip (a small silicon semiconductor crystal) is a small electronic device consisting of the necessary electronicLesson plan 3 teacher notes;
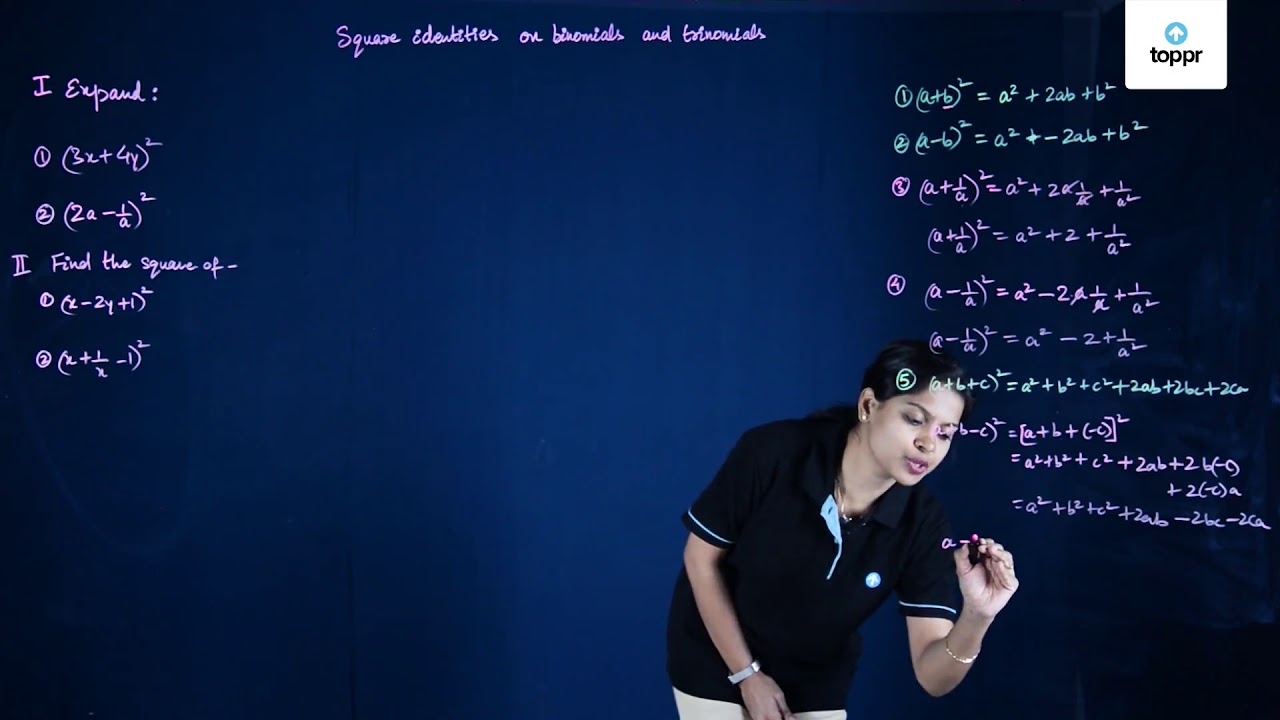



Standard Identities Of Binomials And Trinomials Equations Examples




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
Personality Class 9 Identity (and the Two Streams of Consciousness) Proudly powered by Weebly Home Overview of the System Publications Presentations > > > > > > > Theory of Knowledge Society > Unified Theory Book PT Blog JMU CI Program ContactVolume of cuboid = I x b x h;NCERT Class 9 Maths Lab Manual – Verify the Algebraic Identity (ab)² = a² 2abb² OBJECTIVE To verify the algebraic identity (ab)² = a² 2abb² Materials Required Drawing sheet Pencil Cellotape Coloured papers Cutter Ruler Prerequisite Knowledge Square and its area Rectangle and its area Theory A square is a quadrilateral whose all




Math Worksheet 12 For Class 9 31 07 Friday Class 9 Worksheet 12 English Medium Youtube




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
Sin 3x = 3sin x – 4sin 3 x Trigonometry Formulas From Class 10 to Class 12 Trigonometry Formulas For Class 12 Trigonometry Formulas For Class 11 Trigonometry Formulas For Class 10 Trigonometry Formulas Major systems All trigonometric formulas are divided into two major systems Trigonometric Identities ;How well the class has understood the lesson Finally, we shall learn about special relations called functions 211 Cartesian products of sets Definition Given two nonempty sets A and B, the set of all ordered pairs (x, y), where x ∈ A and y ∈ B is called Cartesian product of A and B;Cubic identity for three variables lesson Theoretical materials and tasks in Mathematics State Board, Class 9



Identity Mathematics Wikipedia




Algebraic Identities For Class 9 Step By Step Guide To Solve Problems
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsComplete Solution of Identity equations Class 9 Notes EduRev chapter (including extra questions, long questions, short questions, mcq) can be found on EduRev, you can check out Class 9 lecture & lessons summary in the same course for Class 9 Syllabus EduRev is like a wikipedia just for education and the Solution of Identity equations Class 9 Notes EduRev images and diagramFree graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problems
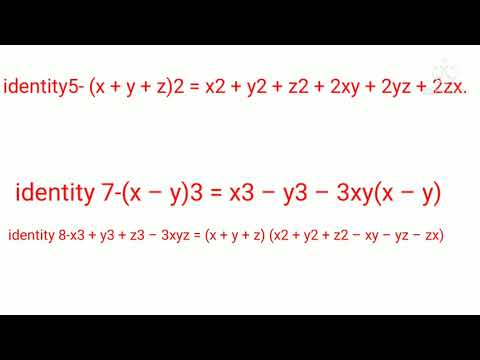



Math Class 9 Ch 2 Polynomial Identity Youtube




Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 9 Learn Cbse Algebraic Expressions Class 8 Expressions
CBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual – Algebraic Identity (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2 To verify the identity (a b) 2 = a 2 2ab b 2 by paper cutting and pasting Area of a square = (side) 2 Area of a rectangle = l x b A sheet of white paper, three sheets of glazed paper (different colours), a pair of scissors, gluestick and a geometry box Identity (x y) 3 = x 3 y 3 3xy(x y) (100 2) 3 = 100 3 2 3 3*100*2(100 2) = 8 600(100 2) = 8 10 = (iii) (998) 3 Identity (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy(x – y) (1000 – 2) 3 = 1000 3 – 2 3 – 3*1000*2(1000 – 2) = – 8 – 6000(1000 – 2) = – 8 – 100 = Factorise each of thePolynomial Identities When we have a sum (difference) of two or three numbers to power of 2 or 3 and we need to remove the brackets we use polynomial identities (short multiplication formulas) (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Example 1 If x = 10, y = 5a (10 5a) 2 = 10 2 2·10·5a (5a) 2 = 100 100a 25a 2




Use Suitable Identities To Find The Following Products I X 4 X 10 Ii X 8 X 10 Ii Youtube




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Ex 9 2 Learn Cbse Algebraic Expressions Class 8 Math
Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions and Identities with Answers Pdf free download Question 3 The expression x y z is in (a) one variable (b) no variable (c) three variables (d) two variables Answer Answer (c) three variables Hint There are three variables x, y and z Question 4 The value of 5x when x = 5 is (a)PlZzz Complete this identity lucky210 lucky210 Math Secondary School answered PlZzz Complete this identity (xy)3 (xy)3 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement (9) Verify (i) x 3 y 3 = (x y) (x 2 − xy y 2) (ii) x 3 – y 3 = (x − y) (x 2 xy y 2) using some nonzero positive integers and check by actual multiplication Can you call these as identites ?




Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A B 3 A3 3a2b 3ab2 Cbse Sample Papers




Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A B 3 A3 3a2b 3ab2 Cbse Sample Papers
The algebraic identities for class 9 consist of identities of all the algebraic formulas and expressions You must have learned algebra formulas for class 9, which are mathematical rule expressed in symbols but the algebraic identities represent that the equation is true for all the values of the variables For example; Therefore, by using the identity (xy) 2 = x 22xyy 2 p 2 –10p25 = (p5) 2 (iii) 25m 2 30m9 Ans Given 25m 2 30m9 Since, 25m 2 , 30m and 9 can be substituted by (5m) 2, 2×5m×3 and 3 2 respectively we get, = (5m) 2 2×5m×3 3 2 Therefore, by using the identity (xy) 2 = x 2 2xyy 2 25m 2 30m9 = (5m3) 2 (iv) 49y 2 84yz36z 2 Ans Given 49y 2 CBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual – Algebraic Identity (a 3 b 3) = (a b) (a 2 – ab b 2) Objective To verify the identity a 3 b 3 = (a b) (a 2 – ab b 2) geometrically by using sets of unit cubes Prerequisite Knowledge Volume of cube = (edge) 3;




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation Of Algebraic Expressions Exercise 5 1




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes
Equations and identities An equation is a statement with an equals sign, stating that two expressions are equal in value, for example \(3x 5 = 11\) Solving anClose 9 Posted by 3 years ago Archived Is x=y an identity? Answer In the given problem, we have to simplify the value of each expression (i) Given We shall use the identity for each bracket x 2 2 y 3 2 z 4 2 2 x 2 y 3 2 y 3 z 4 2 x 2 z 4 By arranging the like terms we get Now adding or




Important Questions For Cbse Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials




Learncbse In Polynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter
Asked my teacher, he couldn't answer itMaterials Required A set of 56 cubes each has dimensions (1 x 1 x 1) cubic unit Cubes may be of Identity VII is a 3 b 3 c 3 − 3abc = (a b c) (a 2 b 2 c 2 − ab − bc − ac) Advertisement Lets take an example a 3 b 3 c 3 − Chapter 3 Class 9 Coordinate Geometry (Term 1) → Facebook Whatsapp Advertisement Identity VIII Identities VIII You are here Ex 25, 9 (i) Ex 25, 10 (i) Important Ex 25,12 Important Deleted for CBSE Board 22 Exams Ex 25,13




Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Mathematics Cbse Topperlearning
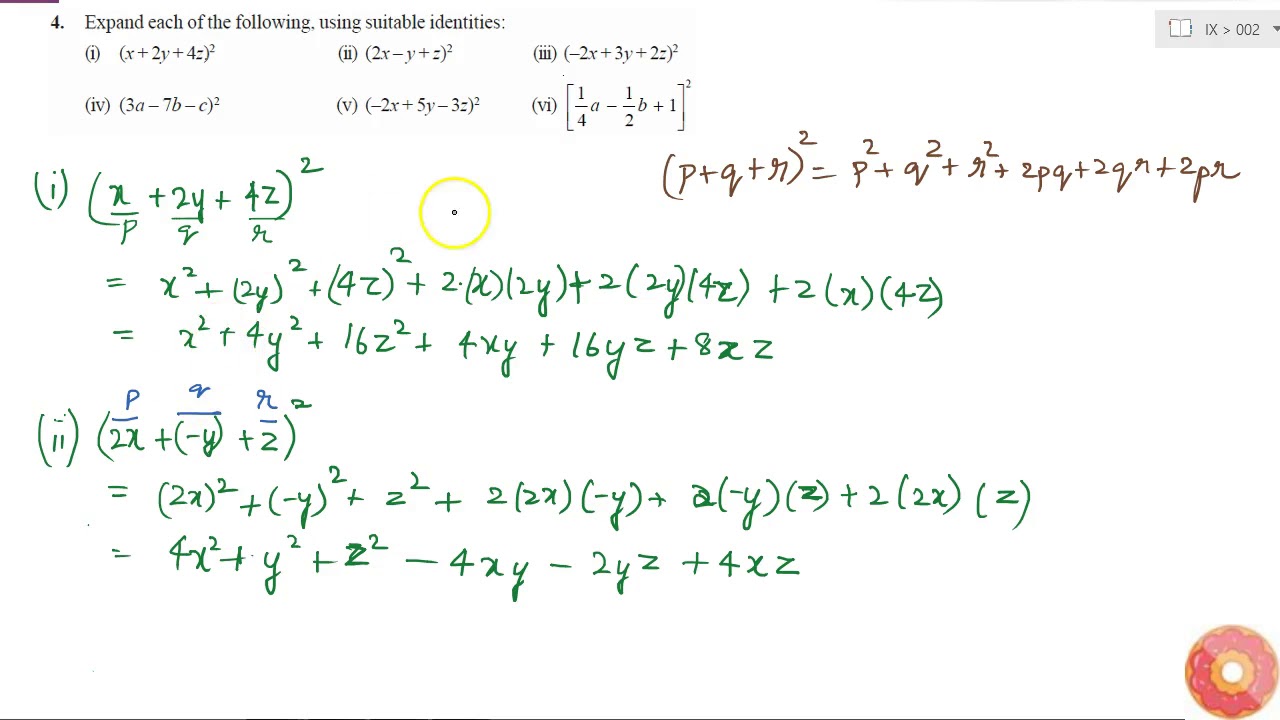



Expand Each Of The Following Using Suitable Identities I X 2y 4z 2 Ii 2x Y Z Youtube
Q4 Expand each of the following, using suitable identities (i) (x 2y 4z) 2 (ii) (2x – y z) 2 (iii) (–2x 3y 2z) 2 (iv) (3a – 7b – c) 2 (v) (–2xCMPS375 Class Notes (Chap03) Page 9 / 28 Dr Kuopao Yang 34 Digital Components 150 FIGURE 39 A Logic Diagram for F(x, y, z) = x y'z 342 Integrated Circuits 151 Gates are not sold individually; Algebraic Expressions and Identities Formulas for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Are you looking for Algebraic Expressions and Identities formulas or important points that are required to understand Algebraic Expressions and Identities for class 8 maths Chapter 9?




What Are The Factors Of X Y 3 X3 Y3 Brainly In




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
3(xy)9(xy) using identity darekarjayshri25 darekarjayshri25 Math Secondary School answered 3(xy)9(xy) using identity 1 See answer darekarjayshri25 is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn pointsIt follows that f x (t) = e tx for every t= (x y)(x 2 y 2 2xy x 2 xy y 2) using identity, (a b) 2 = a 2 b 2 2 ab) = (x y) (3xy) Hence, one of the factor of given polynomial is 3xy Question 18 The coefficient of x in the expansion of (x 3) 3 is (a) 1 (b) 9 (c) 18 (d) 27 Solution (d) Now, (x 3) 3 = x 3 3 3 3x (3)(x 3) using identity, (a b) 3 = a 3 b 3
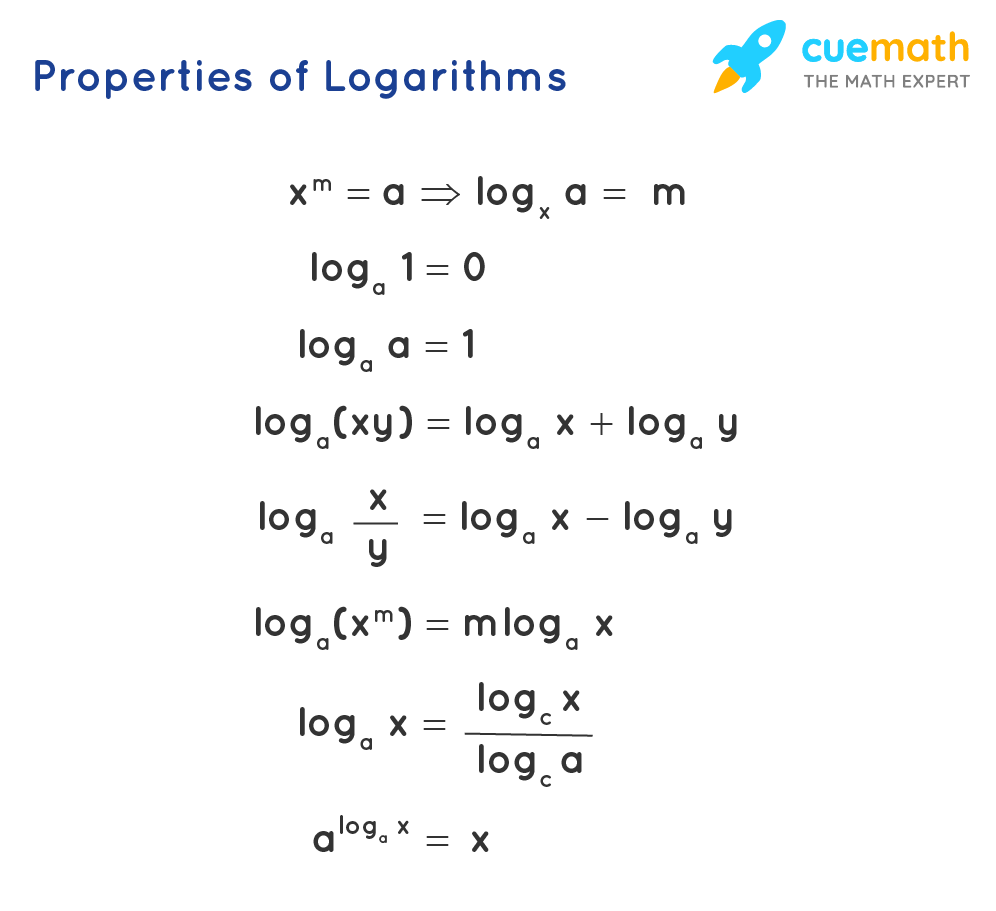



Algebra Formula Solved Examples List Of Algebraic Formulas




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Ex 9 5 Cbsetuts Com
(i) To prove x 3 y 3 = (x y) (x 2 – xy y 2) Now, using identity VI we can say (x y) 3 = x 3 y 3 3xy (xy) Or, (xy) 3You are the right place to get all information about Algebraic Expressions and Identities Class 8 mathsWorksheet 12 Diamond 9;




Example 22 I Write The Cubes In Expanded Form 3a 4b 3




Ncert Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 5 Access Free Pdf
Transcript Ex 25, 9 Verify (i) x3 y3 = (x y) (x2 – xy y2) LHS x3 y3 We know (x y)3 = x3 y3 3xy (x y) So, x3 y3 = (x y)3 – 3xy (x yThe perfect cube forms ( x y) 3 (xy)^3 (xy)3 and ( x − y) 3 ( xy)^3 (x −y)3 come up a lot in algebra We will go over how to expand them in the examples below, but you should also take some time to store these forms in memory, since you'll see them often ( x y) 3 = x 3 3 x 2 y 3 x y 2 y 3 ( x − y) 3 = x 3 − 3 x 2 y 3 NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 21 Question 1 Which one of the following is a polynomial?



Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Maths Geeksforgeeks



1
Worksheet 11 Guess Who;Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution class 10 Verb Articles Some Applications of Trigonometry Real Numbers Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables class 11 Oscillations Redox Reactions Limits and Derivatives Motion in a Plane For example x*y for x in range(10) for y in range(x, x10) To ensure the comprehension always results in a container of the appropriate type, yield and yield from expressions are prohibited in the implicitly nested scope Since Python 36, in an async def function, an async for clause may be used to iterate over a asynchronous iterator A




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2 5 Cbsetuts Com
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 21, 22, 23, 24 and 25 of Polynomials in PDF form Online sols & practice questions This video shows how to evaluate using the identity '(xy)3=x3y33x2y3xy2'To view more Educational content, please visit https//wwwyoutubecom/appuserie1 With One Variable It is an algebraic expression with one variable only Example 5 x, x 2, y – 9, etc 2 With Two Variables It is an algebraic expression with two variables only Example 7 x y, 5 x 2 z, x 2 3 x y 12 y 2, y 2 3 x – 8 y 9, etc 3




Ncert Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 5 Access Free Pdf




Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Maths Geeksforgeeks



1
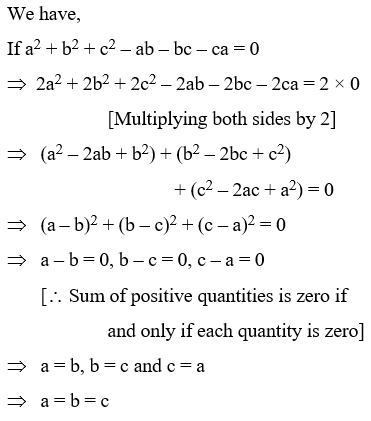



Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
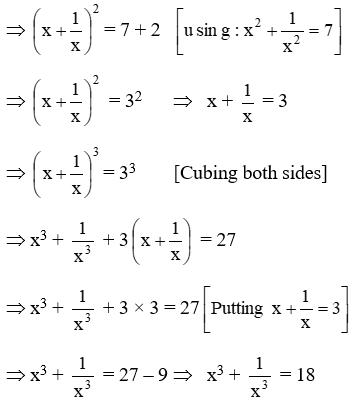



Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper




Ex 2 5 3 Iii Factorise X 2 Y 2 100 Using Appropriate Identities




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities




Class 9 Math Students D5 Youtube




Factorization Of Polynomials Class 9 Ex 2 5 Q13 Ncert Algebraic Identities Solution Ncer Youtube




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Algebraic Identities Exercise 4 3 8 Rdsharmaclass9 Class9solutions Rdsharmaclass9solutions Rd Math Notes Solutions Class




Class 9ncert Solutionschapter 2 Polynomialsexercise 2 5 Solve All Questions And Give Me Answersplease Brainly In




Ex 2 5 9 Verify I X 3 Y 3 X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Teachoo



1




Cbse Class 9 Algebraic Identities Offered By Unacademy



Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Maths Geeksforgeeks




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2 5




Identity Property Of 0 Video Khan Academy
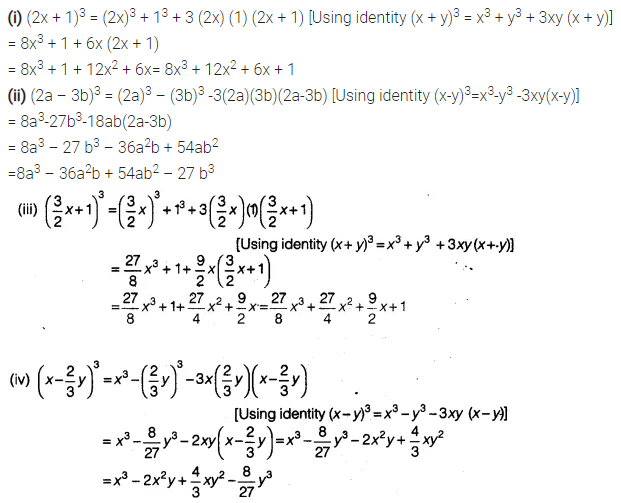



Write The Following Cubes In Expanded Form Cbse Class 9 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




If X Y Z X Y Y Z 9 5 7 Then Find The Values Of X Y Z



Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Mathematics Cbse Topperlearning




Class 9 Polynomials Study Notes And Important Questions Leverage Edu




Algebra Formulas For Class 9 Pdf Download Free Here




Factorisation Of Algebraic Expressions Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions




Verify X3 Y3 And X3 Y3 Std 9 Maths Ex 2 5 Q 9 Youtube




Rd Sharma Ex 4 4 Chapter 4 Class 9 Algebraic Identities Solutions




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Chapter 2 Polynomials Ncert Solutions Class 9 Maths




Factorisation Using Identities Factoring Algebraic Expressions Examples



Expand 1 X Y 3 Whole Cube Studyrankersonline




Ncert Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 5 Access Free Pdf




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Algebraic Identities Exercise Flickr




Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A3 A B Ab B2 Cbse Sample Papers



1
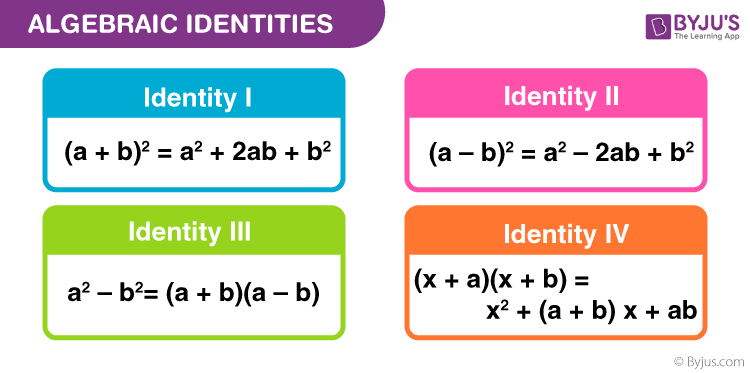



Algebraic Identities Standard Algebraic Identities Definition Examples




How To Verify Algebric Identity X Y 3 X3 3xy X Y Y3 Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com




Ex 9 4 3 Vi Simplify X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Chapter 9 Class 8




Standard Identities Of Binomials And Trinomials Equations Examples




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A B 2 2ab B2 Cbse Sample Papers




Algebraic Expressions And Identities




How To Expand Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Algebraic Expressions And Identities Ex 9 4 Algebraic Expressions Class 8 Expressions




Ex 2 5 12 Verify That X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz 1 2 Ex 2 5




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
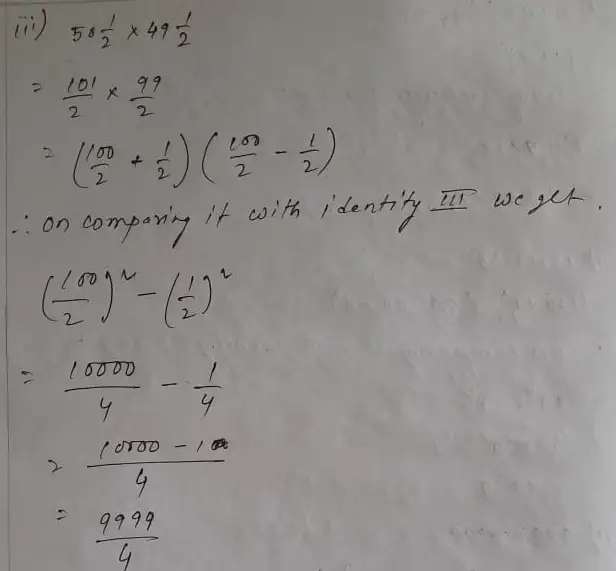



Telangana Scert Class 9 Math Solution Chapter 2 Polynomials And Factorisation Exercise 2 5
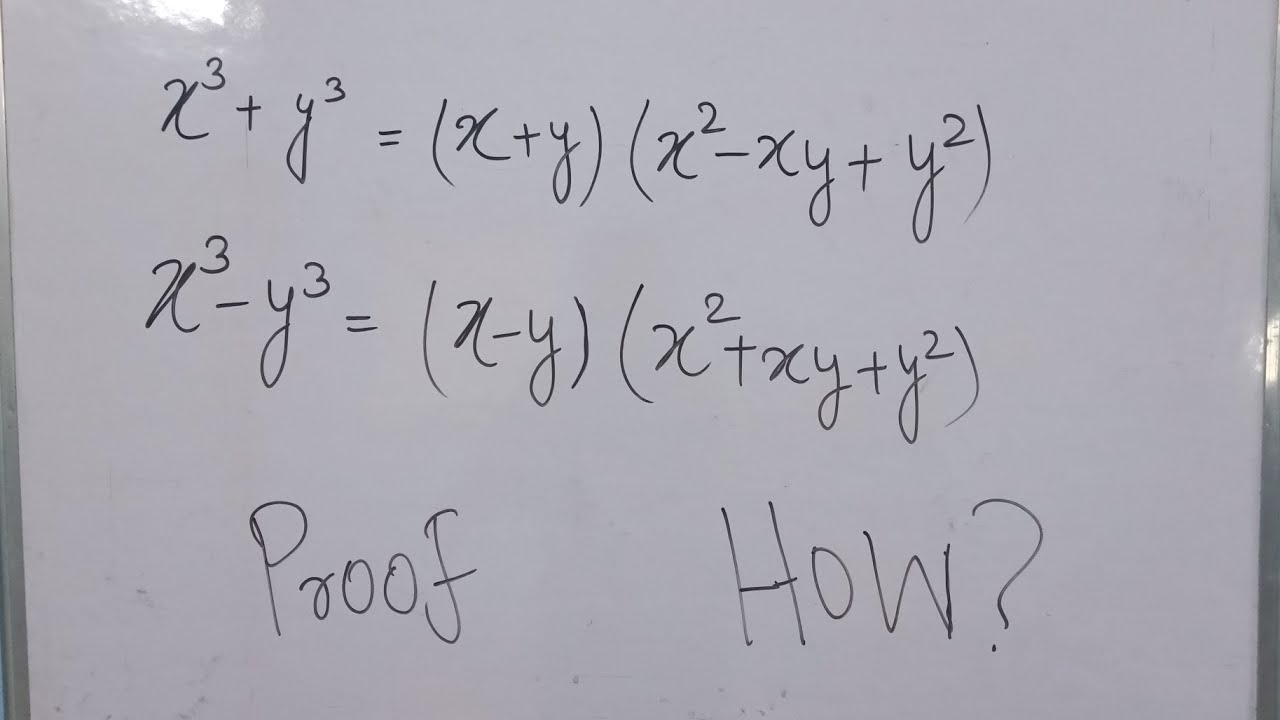



X 3 Y 3 X 3 Y 3 Formula Proof Youtube
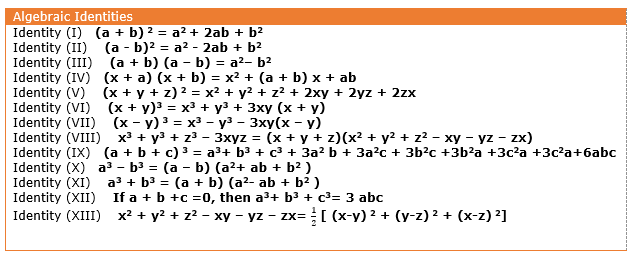



All Useful Algebraic Identities With Proof Examples Physicscatalyst S Blog



Cbse Class 8 Mathematics Algebraic Identities Bridge Course Worksheet




Standard Identities Of Binomials And Trinomials Equations Examples
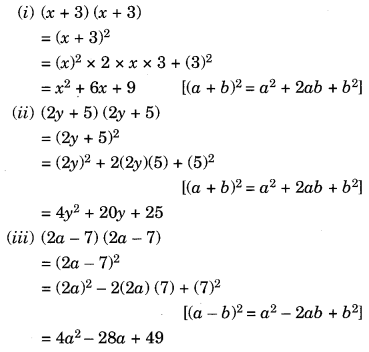



Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Ex 9 5 Learn Cbse




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2 5 Cbsetuts Com




Kseeb Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Polynomials Ex 4 5 Kseeb Solutions




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes
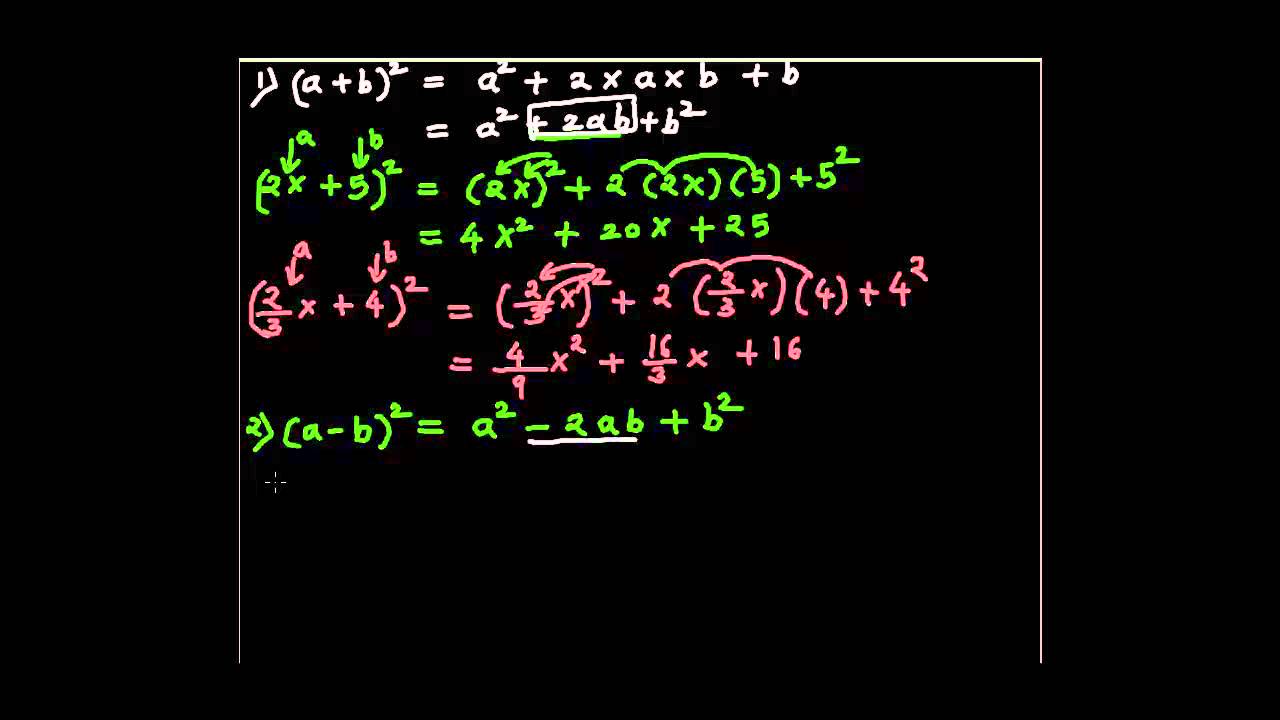



Factorization Using Identities




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 5 Polynomials




Types Of Functions Classification One One Onto Videos And Examples




Ex 2 5 3 I Factorise 9x2 6xy Y2 Using Appropriate Identities




Ex 9 4 3 V Simplify X Y 2x Y X 2y X Y Class 8




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Http Www Aplustopper Com Solving A Quadratic Equation By Factoring Quadratics Maths Solutions Quadratic Equation




Questions On Algebraic Expressions Algebraic Identities Algebraic Formulas



What Is The Formula Of Math A B 3 Math Quora




Factorisation Using Identities Factoring Algebraic Expressions Examples




Solved If X 2 Y 2 49 And X Y 3 Then Find The Value Of X 3 Y 3




Example 12 Using Algebra Identities Find 4p 3q 2 Class 8




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials




Expanding Algebraic Expressions Using Identities Worksheets




Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Maths Geeksforgeeks




Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Ex 9 5
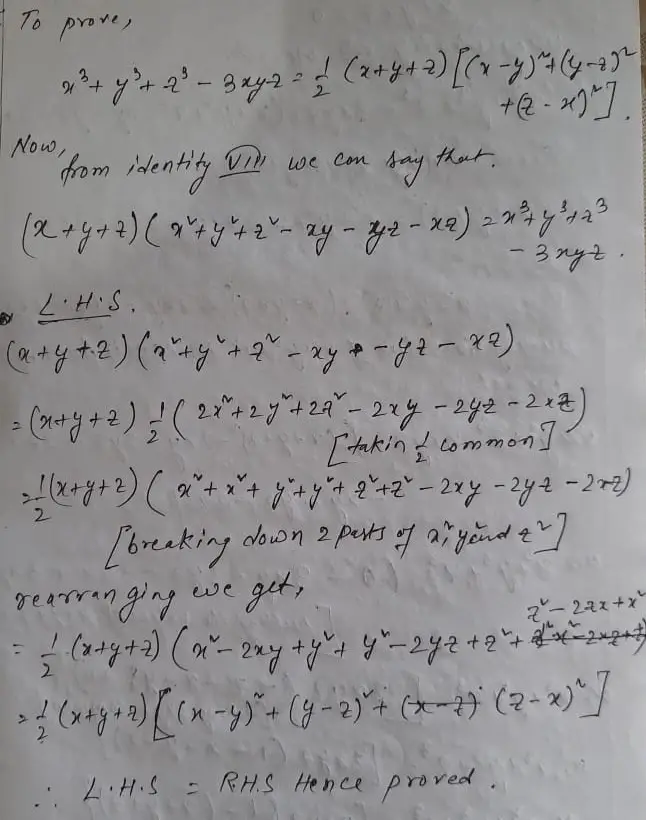



Telangana Scert Class 9 Math Solution Chapter 2 Polynomials And Factorisation Exercise 2 5




Ex 9 5 3 Find The Squares By Using Identities I B 7 2




All Identities Of Class 9 Maths Ch 2 Polynomial Brainly In



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿